What is Open Caching?
- Home
- What is Open Caching?
A New Approach for Streaming:
Many Caches, All Connected
Since the beginning of streaming video, caches have been largely proprietary. Even when developed using open source technologies, like Squid, companies often made unique enhancements and developed their own approaches to hierarchies, session windows, and even the OS TCP stack. Now, with most streaming operators employing multiple CDNs, managing all of the caches across the different networks from a single interface is extremely complex. Open Caching is an attempt to level the paying field so content rights holders, network operators, and CDNs all have visibility into the caching network.
Specifications
Open Caching is defined by a library of documentation which specify the requirements, functions, and programming layer (APIs) of different elements of the Open Caching Network: Nodes, Request Routing, and Control Plane.
Code
In addition to the documentation, the Open Caching work at the Streaming Video Alliance has also produced reference code. These public repos provide a starting point for companies looking to implement Open Caching technologies.
Collaboration
The Open Caching specifications and code weren't developed by a single company. They were the result of a combined effort from dozens of companies since the Alliance's inception.
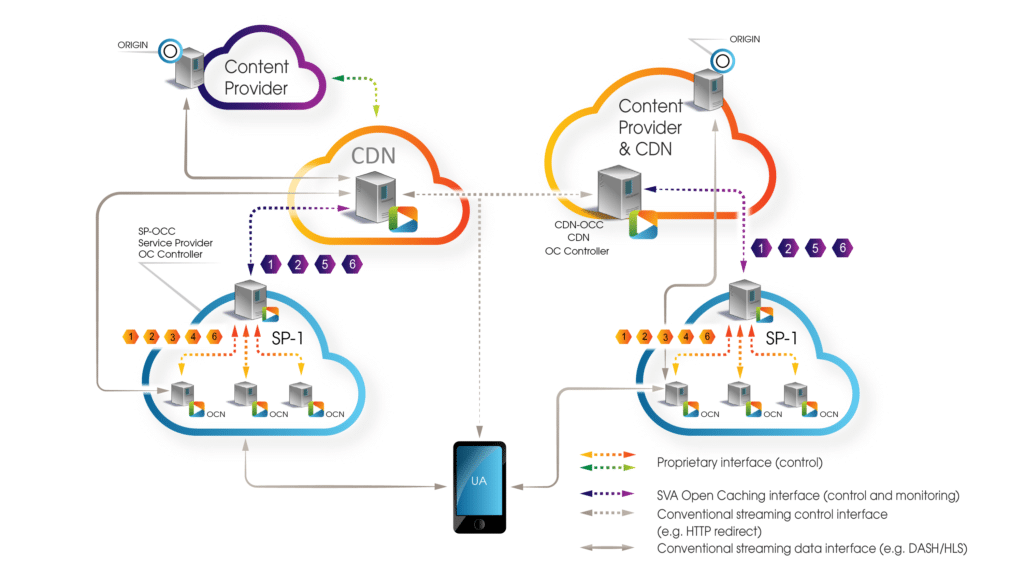
Functional Components
Click on a box to get more detail about the Open Caching component.
Enabling Caching Interoperability
Three key components make up an Open Caching Network.
Caching Nodes
An Open Caching Node represents a caching server, within a content delivery architecture, that complies with Open Caching specifications. The cache can either be built using the specifications (such as for an ISP implementing Open Caching at the edge of their network), or Open Caching functionality can be added through plugins or other means (such as for a Content Delivery Network caches or OTT Platform origins).
Request Router
The Request Router handles the inbound request for content and forwards this request to the appropriate caching node within an environment. The Open Caching specifications identify three methods of routing: DNS, HTTP, and Manifest.
Control Plane
The Control Plane handles all communication related to management of configurations, content purging and pre-positioning, logging, and security. While the Request workflow is focused on the end user’s ability to retrieve content, the Control Plane is focused on how the different members of the video distribution chain are empowered to partake in the delivery process.
The Industry is Beginning to Notice
Open Caching Implementations
Document Spotlight
SVTA2035: Configuration Interface Part 2e: Client Access Control Metadata
This specification adds to the basic client access control metadata in [RFC8006], providing content providers and upstream content delivery networks (uCDNs) extended capabilities in defining location and time window restrictions. Support is also provided to define required Transport Layer Security (TLS) certificates and encryption levels.

